There are countless musical instruments. It is not possible to include each and every musical instrument in this list. But today we will learn about some of the most popular musical instruments which are widely used.
Musical instruments can be into three categories on the basis of how sound is produced through them.
- Wind Instruments
- Percussion Instruments
- String Instruments
Wind Instruments
A wind instrument is a musical instrument with a resonator of some kind, usually a tube. The player blows into (or over) a mouthpiece placed near the end of the resonator to cause a column of air to vibrate. There are plenty of wind instruments such as flute, saxophone, trumpets, trombones, etc. we will be discussing them further in this article.
Percussion Instruments
A musical instrument that produces music or sound when it is struck, scraped or slapped by a beater or when it is struck against another instrument of a like nature is called A percussion instrument. Examples of percussion instruments are tabla, conga, drum, bells, etc.
String Instruments
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that emit a sound when the musician strikes or sounds the strings in some other fashion. Some examples of string instruments are guitar, ukulele, harp, etc.
List of Musical Instruments Names –
- Flute
- Shehnai
- Saxophone
- Bagpipe
- Harmonica
- Trumpet
- Tabla
- Mridangam
- Drum
- Dholak
- Bells
- Xylophone
- Guitar
- Sitar
- Sarangi
- Veena
- Zither
- Cello
- Cornet
- Mandolin
- Organ
- Timpani
- Accordion
- Bugle
- Castanet
- Clarinet
- Marimba
- Oboe
- Ukulele
- Piano
The following is the small description of each musical instrument
Flute
 The flute comes first to mind when we talk about wind musical instrument names. The woodwind family of musical instruments includes the flute. A flute is an aerophone or reedless wind instrument that makes sound by the movement of air across an aperture, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds. It is played by inhaling into a thin edge of a tube with holes that are stopped by the player’s fingers or keys while holding the instrument either vertically or horizontally. Numerous flute players, both experienced and inexperienced, regard James Galway as the world’s greatest and most well-known flutist. Some well-known Indian flute musicians include Pannalal Ghosh and Hari Prasad Chaurasia.
The flute comes first to mind when we talk about wind musical instrument names. The woodwind family of musical instruments includes the flute. A flute is an aerophone or reedless wind instrument that makes sound by the movement of air across an aperture, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds. It is played by inhaling into a thin edge of a tube with holes that are stopped by the player’s fingers or keys while holding the instrument either vertically or horizontally. Numerous flute players, both experienced and inexperienced, regard James Galway as the world’s greatest and most well-known flutist. Some well-known Indian flute musicians include Pannalal Ghosh and Hari Prasad Chaurasia.
Dholak
 Northern India’s Dholak is a very popular folk drum. It is a smaller variant of the dhol and has a basic membrane on the right side. It is barrel-shaped. The inner surface of the left hand’s single membrane has a unique application. This 45 cm long by 27 cm wide musical instrument is commonly used in qawwali, kirtan, lavani, and bhangra.
Northern India’s Dholak is a very popular folk drum. It is a smaller variant of the dhol and has a basic membrane on the right side. It is barrel-shaped. The inner surface of the left hand’s single membrane has a unique application. This 45 cm long by 27 cm wide musical instrument is commonly used in qawwali, kirtan, lavani, and bhangra.
Saxophone
 It is a single-reed woodwind instrument with a conical body that is often made of brass. As with all single-reed instruments, music is created when a reed on a mouthpiece vibrates, creating a sound wave inside the instrument’s body. By adjusting the effective length of the tube by opening and closing perforations in the body, the pitch can be adjusted. Leather pads fastened to player-operated keys seal the perforations. They come in different sizes and are mostly used as transposing instruments. Saxophonists play the saxophone.
It is a single-reed woodwind instrument with a conical body that is often made of brass. As with all single-reed instruments, music is created when a reed on a mouthpiece vibrates, creating a sound wave inside the instrument’s body. By adjusting the effective length of the tube by opening and closing perforations in the body, the pitch can be adjusted. Leather pads fastened to player-operated keys seal the perforations. They come in different sizes and are mostly used as transposing instruments. Saxophonists play the saxophone.
Tabla
 The most well-known percussion instrument from North India is the tabla. Despite being most frequently employed in North Indian classical music, it has spread over all musical genres and is now the most widely used percussion instrument in India. Zakir Hussain, Allah Rakha, Sabir Khan, Pt. Kishan Maharaj, Pt. Jnan Prakash Ghosh, and Sandeep Das are well-known tabla players.
The most well-known percussion instrument from North India is the tabla. Despite being most frequently employed in North Indian classical music, it has spread over all musical genres and is now the most widely used percussion instrument in India. Zakir Hussain, Allah Rakha, Sabir Khan, Pt. Kishan Maharaj, Pt. Jnan Prakash Ghosh, and Sandeep Das are well-known tabla players.
Mridangam
 Ancient percussion instruments like the mridangam are being used today. In a Carnatic music group, it serves as the main source of rhythmic support. The pakhawaj is the main percussion instrument of Dhrupad, a modified version of the original. Played in Maritime Southeast Asia, the Kendang is a comparable instrument.
Ancient percussion instruments like the mridangam are being used today. In a Carnatic music group, it serves as the main source of rhythmic support. The pakhawaj is the main percussion instrument of Dhrupad, a modified version of the original. Played in Maritime Southeast Asia, the Kendang is a comparable instrument.
Drum
 The drum is a percussion instrument that produces sound when it is pounded with sticks or hands. It often has a taut membrane covering one or both ends and is cylindrical, barrel-shaped, or bowl-shaped. Ringo Starr, John Bonham, Ginger Baker, Keith Moon, Neil Peart, Buddy Rich, Gene Krupa, and Sivamani are some of a few well-known drummers.
The drum is a percussion instrument that produces sound when it is pounded with sticks or hands. It often has a taut membrane covering one or both ends and is cylindrical, barrel-shaped, or bowl-shaped. Ringo Starr, John Bonham, Ginger Baker, Keith Moon, Neil Peart, Buddy Rich, Gene Krupa, and Sivamani are some of a few well-known drummers.
Bagpipe
 The sound of the bagpipe is produced by the wind pressure that is released from a bag that is squeezed by the player’s arm. It has reed pipes. While bagpipes are most often associated with Scotland, they are also employed in various forms throughout Europe and western Asia, including in the folk music of Ireland, Northumberland, and France.
The sound of the bagpipe is produced by the wind pressure that is released from a bag that is squeezed by the player’s arm. It has reed pipes. While bagpipes are most often associated with Scotland, they are also employed in various forms throughout Europe and western Asia, including in the folk music of Ireland, Northumberland, and France.
Bells
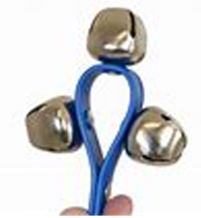 A bell is a hollow metal item, often shaped like a deep inverted cup that widens at the mouth, that when struck, notably by a clapper within, produces a distinct musical note.
A bell is a hollow metal item, often shaped like a deep inverted cup that widens at the mouth, that when struck, notably by a clapper within, produces a distinct musical note.
Guitar
 Usually having six strings, the guitar is a fretted musical instrument. It is often held flat against the player’s body and played by plucking or strumming the strings with the hand while simultaneously pressing a few strings against the frets with the fingers of the opposing hand. To strike the strings, one can use a plectrum or a few individual finger picks. A guitar’s resonant chamber projects the guitar’s sound acoustically; alternatively, an electronic pickup and an amplifier amplify the sound.
Usually having six strings, the guitar is a fretted musical instrument. It is often held flat against the player’s body and played by plucking or strumming the strings with the hand while simultaneously pressing a few strings against the frets with the fingers of the opposing hand. To strike the strings, one can use a plectrum or a few individual finger picks. A guitar’s resonant chamber projects the guitar’s sound acoustically; alternatively, an electronic pickup and an amplifier amplify the sound.
Shehnai
 Similar in many ways to the western oboe, the shehnai is a reed instrument. It has a strong, characteristic nasal quality, and its sound is fairly loud. It is made by blowing the reeds, which are linked together and tensed slightly between the lips. By adjusting the lips’ and air’s pressure, the pitch can be changed. Famous Shehnai players include Ali Ahmad Hussain, Krishna Ram Chaudhary, and Bismillah Khan.
Similar in many ways to the western oboe, the shehnai is a reed instrument. It has a strong, characteristic nasal quality, and its sound is fairly loud. It is made by blowing the reeds, which are linked together and tensed slightly between the lips. By adjusting the lips’ and air’s pressure, the pitch can be changed. Famous Shehnai players include Ali Ahmad Hussain, Krishna Ram Chaudhary, and Bismillah Khan.
Sitar
 The sitar is an Indian musical instrument with a long neck and a round body similar to a guitar. The Persian roots of the word “sitar” are “si,” which means “three,” and “tar,” which means “thread.” Sitar players who are well-known include Pt. Ravi Shankar, Shahid Parvez Khan, Budhaditya Mukherjee, and Anushka Shankar.
The sitar is an Indian musical instrument with a long neck and a round body similar to a guitar. The Persian roots of the word “sitar” are “si,” which means “three,” and “tar,” which means “thread.” Sitar players who are well-known include Pt. Ravi Shankar, Shahid Parvez Khan, Budhaditya Mukherjee, and Anushka Shankar.
Sarangi
 The srang is a short-necked, bowed string instrument from the Indian subcontinent that is utilized in both Pakistani and Hindustani classical music. It is claimed to sound most like the human voice and be capable of mimicking vocal embellishments like gamaks and meends. Shakoor Khan, Pt. Ram Narayan, Ramesh Mishra, and Sultan Khan are a few well-known sarangi musicians.
The srang is a short-necked, bowed string instrument from the Indian subcontinent that is utilized in both Pakistani and Hindustani classical music. It is claimed to sound most like the human voice and be capable of mimicking vocal embellishments like gamaks and meends. Shakoor Khan, Pt. Ram Narayan, Ramesh Mishra, and Sultan Khan are a few well-known sarangi musicians.
Harmonica
 The harmonica, commonly known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free-reed brass instrument utilized in various musical genres around the world, particularly in jazz, country, rock, blues, and American folk music. Diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, symphonic, and bass harmonicas are among the numerous variations. When playing harmonica, the player blows air into or out of one or more holes along the mouthpiece using their lips and tongue. A chamber with at least one reed can be found behind each hole. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring that is often composed of bronze, brass, or stainless steel and is fastened over an airway at one end.
The harmonica, commonly known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free-reed brass instrument utilized in various musical genres around the world, particularly in jazz, country, rock, blues, and American folk music. Diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, symphonic, and bass harmonicas are among the numerous variations. When playing harmonica, the player blows air into or out of one or more holes along the mouthpiece using their lips and tongue. A chamber with at least one reed can be found behind each hole. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring that is often composed of bronze, brass, or stainless steel and is fastened over an airway at one end.
Veena
 The traditional instrument of India, the veena, is also known as the Saraswati veena, a South Indian musical instrument. Veena is a plucked stringed classical instrument that is typically used to accompany Carnatic music. Various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent make up the veena, often written vina.
The traditional instrument of India, the veena, is also known as the Saraswati veena, a South Indian musical instrument. Veena is a plucked stringed classical instrument that is typically used to accompany Carnatic music. Various chordophone instruments from the Indian subcontinent make up the veena, often written vina.
Zither
 Zither is a class of stringed instruments. The European zither is made up of 30 or 40 gut or metal strings that are stretched across a narrow, flat sound chamber. The plectrum worn on the right thumb is used to pluck the strings closest to the player, which are located above a fretted fingerboard and are stopped by the left hand to generate melodic notes. The distant strings, which are still unstopped, are played in accompaniment at the same time by the right hand’s fingers. The zither is set up on a table or across the player’s knees.
Zither is a class of stringed instruments. The European zither is made up of 30 or 40 gut or metal strings that are stretched across a narrow, flat sound chamber. The plectrum worn on the right thumb is used to pluck the strings closest to the player, which are located above a fretted fingerboard and are stopped by the left hand to generate melodic notes. The distant strings, which are still unstopped, are played in accompaniment at the same time by the right hand’s fingers. The zither is set up on a table or across the player’s knees.
Cello

A bowed string instrument belonging to the violin family is the cello or violoncello. Its four strings, which are often tuned in perfect fifths, are C2, G2, D3, and A3, from low to high. All the four strings on the viola are an octave higher. The bass clef, sometimes known as the alto clef, and treble clef are typically employed for sections with higher dynamic ranges in cello music.
Cornet
 It is a musical instrument that looks like the trumpet but differs from it. It has a conical bore, a more condensed shape, and a mellower tone. There are cornets in A, C, and a soprano cornet in addition to the transposing cornet that is most frequently used. The Renaissance and early Baroque cornett are unconnected to all of them.
It is a musical instrument that looks like the trumpet but differs from it. It has a conical bore, a more condensed shape, and a mellower tone. There are cornets in A, C, and a soprano cornet in addition to the transposing cornet that is most frequently used. The Renaissance and early Baroque cornett are unconnected to all of them.
Mandolin
 Typically plucked with a plectrum, the mandolin is a stringed instrument belonging to the lute family. Although there are additional variations with five (10 strings) and six (12) course tunings, it most frequently has four courses of doubled metal strings tuned in unison, giving it a total of eight strings. Typically, the courses are tuned to a perfect fifth interval, similar to how a violin is tuned (G3, D4, A4, E5). It is from the same class as the violin and the mandola, octave mandolin, mandocello, and mandobass. This musical instrument is a soprano member.
Typically plucked with a plectrum, the mandolin is a stringed instrument belonging to the lute family. Although there are additional variations with five (10 strings) and six (12) course tunings, it most frequently has four courses of doubled metal strings tuned in unison, giving it a total of eight strings. Typically, the courses are tuned to a perfect fifth interval, similar to how a violin is tuned (G3, D4, A4, E5). It is from the same class as the violin and the mandola, octave mandolin, mandocello, and mandobass. This musical instrument is a soprano member.
Organ
 An organ is a musical instrument that is played with the hands and feet of the player. Pressurized air is passed through a series of pipes that are arranged in scalelike rows to produce the notes. Organs include reed organs and electronic organs, but unless otherwise stated, the term is typically used to refer to pipe organs. The organ has the most extensive history of any musical instrument and the oldest and greatest extant repertory of any instrument used in Western music, despite being one of the most difficult instruments available.
An organ is a musical instrument that is played with the hands and feet of the player. Pressurized air is passed through a series of pipes that are arranged in scalelike rows to produce the notes. Organs include reed organs and electronic organs, but unless otherwise stated, the term is typically used to refer to pipe organs. The organ has the most extensive history of any musical instrument and the oldest and greatest extant repertory of any instrument used in Western music, despite being one of the most difficult instruments available.
Timpani
 Kettledrums, often known as timpani, are percussion instruments. They are made out of a head, which is a membrane, stretched over a sizable bowl, which is typically made of copper. Thus, the timpani is an example of a kettle drum, also known as a vessel drum or a semispherical drum, and has a body that resembles a portion of a sphere with a cut that conforms to the head. A specific drum stick called a timpani stick, or timpani mallet, is used to play them by striking the head on the instrument. They are utilized in many different kinds of groupings nowadays, including concert bands, marching bands, orchestras, and even certain rock bands.
Kettledrums, often known as timpani, are percussion instruments. They are made out of a head, which is a membrane, stretched over a sizable bowl, which is typically made of copper. Thus, the timpani is an example of a kettle drum, also known as a vessel drum or a semispherical drum, and has a body that resembles a portion of a sphere with a cut that conforms to the head. A specific drum stick called a timpani stick, or timpani mallet, is used to play them by striking the head on the instrument. They are utilized in many different kinds of groupings nowadays, including concert bands, marching bands, orchestras, and even certain rock bands.
Accordions
 A family of bellows-driven free-reed aerophones known as squeezeboxes, accordions are box-shaped musical instruments. The harmonium and American reed organ belong to the same family as an accordion, although they are often larger and sit on a surface or the floor.
A family of bellows-driven free-reed aerophones known as squeezeboxes, accordions are box-shaped musical instruments. The harmonium and American reed organ belong to the same family as an accordion, although they are often larger and sit on a surface or the floor.
The accordion is played by compressing or expanding the bellows while depressing buttons or keys, which opens pallets and allows air to travel through strips of brass or steel, known as reeds. Inside the body, they vibrate to create sound. The performer often plays the bass or preset chord buttons on the left side and the melody on the right (known as the manual).
Bugle
 One of the most basic brass instruments, the bugle often lacks valves or other pitch-altering mechanisms. Changing the player’s embouchure is the only way to control pitch.
One of the most basic brass instruments, the bugle often lacks valves or other pitch-altering mechanisms. Changing the player’s embouchure is the only way to control pitch.
Castanets
 Castanets, commonly referred to as clackers or palillos, are a type of idiophone utilized in music from several cultures, including Spanish, Kalo, Moorish, Ottoman, Italian, Sephardic, Swiss, and Portuguese. A comparable tool known as the crotalum was used in ancient Greece and Rome. A string connects a pair of concave shells on one edge, creating the instrument. They are used to provide a rapid succession of clicks to create a ripping or rattling sound while being held in hand. Despite fiberglass becoming more and more fashionable, they are often fashioned from hardwood.
Castanets, commonly referred to as clackers or palillos, are a type of idiophone utilized in music from several cultures, including Spanish, Kalo, Moorish, Ottoman, Italian, Sephardic, Swiss, and Portuguese. A comparable tool known as the crotalum was used in ancient Greece and Rome. A string connects a pair of concave shells on one edge, creating the instrument. They are used to provide a rapid succession of clicks to create a ripping or rattling sound while being held in hand. Despite fiberglass becoming more and more fashionable, they are often fashioned from hardwood.
Clarinets
 A single-reed woodwind instrument is a clarinet. Clarinets, like many wind instruments, come in a variety of sizes, each with its own pitch range. They all use a mouthpiece with a single reed and feature bells that are flared and nearly cylindrical in shape. The clarinet is a common instrument in jazz, klezmer, concert bands, military bands, marching bands, and classical music, among other genres.
A single-reed woodwind instrument is a clarinet. Clarinets, like many wind instruments, come in a variety of sizes, each with its own pitch range. They all use a mouthpiece with a single reed and feature bells that are flared and nearly cylindrical in shape. The clarinet is a common instrument in jazz, klezmer, concert bands, military bands, marching bands, and classical music, among other genres.
Trumpet
 A trumpet is a bell-shaped brass instrument that produces a loud, piercing tone. In jazz and classical ensembles, this musical instrument is frequently used. The tube is coiled to create a coil with three valves that have a straight side. One of the most well-known trumpeters in the world is Wynton Marsalis. The piccolo trumpet, which has the highest register in the brass family, and the bass trumpet, which is pitched an octave below the ordinary B or C trumpet, are both included in the trumpet category.
A trumpet is a bell-shaped brass instrument that produces a loud, piercing tone. In jazz and classical ensembles, this musical instrument is frequently used. The tube is coiled to create a coil with three valves that have a straight side. One of the most well-known trumpeters in the world is Wynton Marsalis. The piccolo trumpet, which has the highest register in the brass family, and the bass trumpet, which is pitched an octave below the ordinary B or C trumpet, are both included in the trumpet category.
Marimba
 The marimba is a percussion-family musical instrument made out of wooden bars that are pounded by mallets. A resonator pipe that amplifies certain harmonics of the sound produced by each bar is located below it. The tone of the marimba is warmer and purer than that of the xylophone. Additionally, its range is often smaller than a xylophone’s. Usually, a marimba’s bars are arranged chromatically, much like a piano’s keys. Idiophones include the marimba.
The marimba is a percussion-family musical instrument made out of wooden bars that are pounded by mallets. A resonator pipe that amplifies certain harmonics of the sound produced by each bar is located below it. The tone of the marimba is warmer and purer than that of the xylophone. Additionally, its range is often smaller than a xylophone’s. Usually, a marimba’s bars are arranged chromatically, much like a piano’s keys. Idiophones include the marimba.
| Read more: What is the Best Age to Learn to Sing? |
The marimba is still played today as a solo instrument or in a variety of conventional ensembles, including orchestras, marching bands, percussion ensembles, brass and concert bands, and others.
Xylophone
 A xylophone is a percussion-family musical instrument that uses wooden bars and mallets to produce sound. Similar to the glockenspiel, the xylophone is simply made up of a set of tuned keys set up like a piano keyboard. Each bar is an idiophone set to a certain pitch of a musical scale, whether it is chromatic for orchestral use or pentatonic or heptatonic in the case of many African and Asian instruments.
A xylophone is a percussion-family musical instrument that uses wooden bars and mallets to produce sound. Similar to the glockenspiel, the xylophone is simply made up of a set of tuned keys set up like a piano keyboard. Each bar is an idiophone set to a certain pitch of a musical scale, whether it is chromatic for orchestral use or pentatonic or heptatonic in the case of many African and Asian instruments.
Oboe

An example of a double-reed woodwind instrument is the oboe. Mostly wood is used to make oboes. It can also be built of synthetic materials such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The soprano or treble register is where the oboe is most frequently heard.
Ukulele
 A stringed instrument with a shape resembling a miniature guitar is known as a ukulele. As a result of the strings’ softness and comfort for the fingers, its four nylon strings make it incredibly simple to play (as compared to a guitar). Both beginners and experts will find it to be a very useful device.
A stringed instrument with a shape resembling a miniature guitar is known as a ukulele. As a result of the strings’ softness and comfort for the fingers, its four nylon strings make it incredibly simple to play (as compared to a guitar). Both beginners and experts will find it to be a very useful device.
The strings of a ukulele are tuned similarly to the first four strings of a guitar, but because of the shorter scale length, the notes are a little higher.
The instrument’s size and construction affect its volume and tone. Soprano, concert, tenor, and baritone are the four standard sizes of ukuleles.
Piano
 It is a stringed keyboard instrument in which softer-coated wooden hammers are used to strike the strings. With the fingers of both hands, the performer presses or hits a series of keys (little levers) on a keyboard to make the hammers strike the strings. Around the year 1700, Bartolomeo Cristofori created it in Italy.
It is a stringed keyboard instrument in which softer-coated wooden hammers are used to strike the strings. With the fingers of both hands, the performer presses or hits a series of keys (little levers) on a keyboard to make the hammers strike the strings. Around the year 1700, Bartolomeo Cristofori created it in Italy.
Musical instrument names list is unending as every corner of the world has its own musical instrument in some or other modified way or name. In this musical instrument names list, we tried to cover some of the most popular and widely used instruments.
Other Important Links
Learn Lyric Writing from Sameer Anjaan
Learn singing online with Monali Thakur
Join Unlu Lyric Writing Fellowship and Become the next great Lyricist
Join Unlu Community of Lyricists, Singers, Composers, and Producers
Mugafi
Create captivating stories, iconic characters, and legendary universes for the world to witness.
Building a library of high-quality Stories, Novels & Screenplays
Your ultimate co-pilot for turning your imagination into pitch-perfect stories.
Transform your writing instantly with Ved; conducting research, rewriting scenes, expanding dialogues, and more.
Ensure script readiness with our advanced algorithms processing millions of data points, and delivering top-quality scores for pitch-perfect narratives.
Experience seamless teamwork, with built-in collaboration tools, sharing real-time feedback to enhance your co-writing journey.
Format your content flawlessly with easy-to-use customisable shortcuts, ensuring it’s production-house-ready and free from rejection.
Mugafi Ved – AI screenwriting tool
Email: hello@mugafi.com








1 Comment
this article helped me a lot to know about the top 10 musical instrument of India. THANKS a lot.